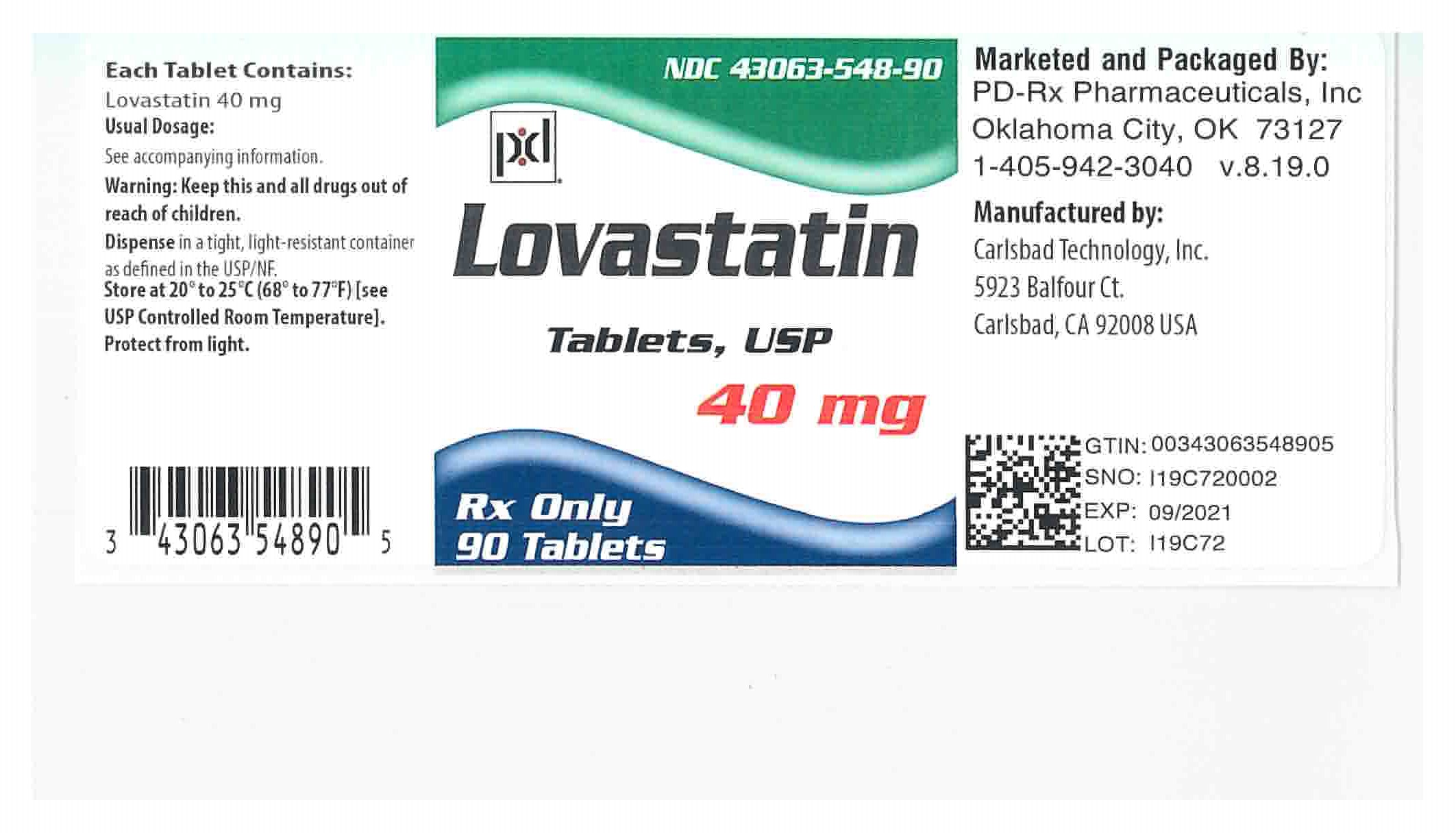
Begin treatment with Lovastatin at a dose of 20 mg once daily in the evening. This initial dosage allows the medication to effectively lower cholesterol levels while monitoring the patient’s response. Adjustments may be made after four weeks based on lipid panel results and tolerability.
For patients needing more significant cholesterol reduction, increase the daily dose to 40 mg, also taken in the evening. The maximum recommended dose is 80 mg per day, but this should only be considered for those who have not achieved treatment goals at lower doses and who can tolerate the medication well.
Always take Lovastatin with a full glass of water. If a dose is missed, take it as soon as you remember, provided it is not close to the next scheduled dose. Never double the dose to catch up. Regular monitoring of liver enzymes and muscle-related symptoms is essential during treatment to prevent potential side effects.
Key considerations: Limit grapefruit juice consumption while on Lovastatin as it can interact with the medication, increasing the risk of side effects. Communicate with your healthcare provider about all other medications being taken to avoid harmful interactions.
- Lovastatin Dosage and Administration
- Administration Guidelines
- Understanding Lovastatin: An Overview
- Recommended Dosage for Adults
- Adjustments Based on Individual Needs
- Considerations for Specific Populations
- Dosage Adjustments for Renal Impairment
- Mild to Moderate Renal Impairment
- Severe Renal Impairment
- Administration Guidelines for Effective Use
- Starting Dosage
- Consistency in Administration
- Timing of Lovastatin Doses for Optimal Efficacy
- Potential Interactions Affecting Dosage
- Consideration of Grapefruit Juice
- Interactions with Other Statins
- Monitoring and Follow-up: Ensuring Safe Usage
Lovastatin Dosage and Administration
The recommended starting dose of lovastatin for adults is typically 20 mg once daily, preferably taken with the evening meal to enhance absorption. Depending on individual cholesterol levels and response to therapy, the dose may be adjusted. Increases should be made at intervals of 4 weeks or more, with the maximum allowable dose being 80 mg per day, divided into two doses if necessary.
For elderly patients or those with renal impairment, initiate treatment with caution. A lower starting dose of 10 mg is advisable, with gradual adjustments based on tolerance and lipid response. Monitoring liver function tests is recommended before starting and during treatment, as the risk of liver enzyme elevation exists.
Administration Guidelines
Take lovastatin orally at the same time each day to maintain consistent levels in the bloodstream. Swallow the tablets whole; do not crush or chew. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it is close to the time of your next dose. In that case, skip the missed dose and resume your regular schedule. Avoid double dosing.
Alcohol consumption can raise blood levels of lovastatin, so moderation is advised. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting or stopping lovastatin or any other medications to avoid potential interactions.
Understanding Lovastatin: An Overview
Lovastatin reduces cholesterol levels effectively. It inhibits HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme responsible for cholesterol synthesis in the liver. A lower cholesterol level can decrease the risk of cardiovascular diseases significantly.
It’s crucial to monitor liver function while taking Lovastatin. Regular blood tests should be scheduled every few months during the first year of treatment to ensure the liver is handling the medication safely.
Dosage typically starts at 20 mg once daily in the evening. Depending on individual cholesterol levels and response to the treatment, doctors may adjust the dosage. The maximum recommended dose is 80 mg per day, but this requires careful consideration due to potential side effects.
The medication is available in tablet form and should be taken with food to enhance absorption. Fasting before taking the dose may reduce its efficacy.
Drug interactions can amplify Lovastatin’s effects or increase the risk of side effects. Patients should inform their healthcare provider about all medications and supplements they are currently taking. Grapefruit juice should be avoided, as it can elevate Lovastatin levels in the bloodstream.
Side effects may include headache, gastrointestinal discomfort, and muscle pain. Severe reactions, although rare, can occur. Immediate medical attention is necessary if muscle pain is accompanied by fever or dark urine, indicating a potential condition called rhabdomyolysis.
| Dosing Information | Notes |
|---|---|
| Initial dose | 20 mg once daily in the evening |
| Maximum dose | 80 mg per day, under strict supervision |
| Administration | Take with food for best absorption |
| Monitoring | Regular liver function tests recommended |
Adhering to prescribed dosages and maintaining open communication with a healthcare provider can optimize the benefits of Lovastatin while minimizing risks. Always discuss any changes in health status or new symptoms while on this medication.
Recommended Dosage for Adults
The typical starting dose of Lovastatin for adults is 20 mg once daily, preferably in the evening. This allows for optimal absorption and efficacy.
Adjustments Based on Individual Needs
- After 4 to 6 weeks, your healthcare provider may assess your cholesterol levels and adjust the dose as needed.
- Based on the response to treatment, the dose can be increased to 40 mg once daily.
- The maximum recommended dose is 80 mg per day, divided into two doses of 40 mg each, taken in the evening.
Considerations for Specific Populations
- In elderly patients or those with renal impairment, the dose may require careful adjustment, starting at a lower level.
- Patients taking other medications that may interact with Lovastatin should consult their healthcare provider for tailored dosing recommendations.
- Always follow your doctor’s instructions regarding dosage and administration to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Regular follow-ups with blood tests to monitor cholesterol levels and liver function are advised during treatment. Adjustments should not be made without consulting your healthcare provider.
Dosage Adjustments for Renal Impairment
For patients with renal impairment, dosage adjustments of lovastatin are often necessary to minimize the risk of adverse effects. The following recommendations ensure safe administration:
Mild to Moderate Renal Impairment
- In patients with mild to moderate renal impairment (CrCl 30-59 mL/min), initiate treatment with a lower dose of lovastatin. Start at 20 mg once daily.
- Monitor renal function regularly and adjust the dose based on therapeutic response and tolerability.
Severe Renal Impairment
- Avoid lovastatin in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl < 30 mL/min). Other lipid-lowering medications are preferred in this population.
- If lovastatin must be used, consult with a healthcare provider for careful consideration of the risk versus benefit.
Always consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to lovastatin dosage based on renal function. Close monitoring is advised to prevent potential complications.
Administration Guidelines for Effective Use
Take Lovastatin in the evening with meals to enhance absorption. This timing aligns with the body’s natural cholesterol production cycle, optimizing the medication’s efficacy. Swallow the tablet whole; do not crush or chew, as this may alter the drug’s effectiveness.
Starting Dosage
Begin with a dose of 20 mg daily. Your healthcare provider may adjust this based on cholesterol levels and individual response. Regular monitoring of lipid levels is essential to determine the appropriate dosage for you.
Consistency in Administration
Maintain a consistent schedule for taking Lovastatin. Regular dosing helps keep the drug levels stable in your body, providing a steady benefit. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember. If it’s almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose. Never take an extra dose to make up for the one missed.
Always consult your healthcare professional before making any adjustments to your dosage. Avoid abrupt changes without guidance, as this may impact treatment outcomes.
Timing of Lovastatin Doses for Optimal Efficacy
Take lovastatin in the evening, as this timing aligns with the body’s natural cholesterol production cycle, maximizing its effectiveness. Administer the dose with food to enhance absorption and minimize gastrointestinal discomfort.
The common dosing range is between 20 mg to 80 mg per day. If prescribed a higher dose, split it into two smaller doses taken in the evening with dinner. This approach helps maintain more consistent drug levels in the bloodstream.
Consistency in timing also plays a key role. Aim to take lovastatin at the same time every day. This practice not only aids in forming a routine but also promotes medication adherence.
Monitor your cholesterol levels regularly to evaluate the response to treatment and adjust the timing or dosage as needed, based on your healthcare provider’s advice.
Potential Interactions Affecting Dosage
Several medications can influence the efficacy and safety of lovastatin. Adjusting lovastatin dosage may be necessary when taken alongside specific drugs. Notably, strong inhibitors of the CYP3A4 enzyme significantly increase lovastatin levels, heightening the risk of side effects such as myopathy or rhabdomyolysis. Common inhibitors include ketoconazole, itraconazole, erythromycin, and certain HIV protease inhibitors. It is advisable to avoid concurrent use of these medications or to carefully monitor and potentially reduce the lovastatin dose.
Consideration of Grapefruit Juice
Grapefruit juice is also a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor that can lead to elevated levels of lovastatin. Patients should limit or avoid grapefruit juice while on lovastatin therapy to maintain optimal drug levels and minimize adverse effects.
Interactions with Other Statins
Drug interactions extend to other statins, as combining lovastatin with other cholesterol-lowering agents that share metabolic pathways can lead to compounded effects. Monitor patients who take lovastatin with simvastatin or atorvastatin closely and consider dosage adjustments or alternative therapies as necessary.
Monitoring and Follow-up: Ensuring Safe Usage
Schedule regular follow-up appointments to assess the patient’s response to lovastatin. Initiate monitoring of lipid levels approximately 4-12 weeks after starting therapy or adjusting the dose. Aim for target LDL cholesterol levels as recommended by healthcare guidelines.
Monitor liver function tests before initiating treatment and periodically thereafter, especially if the patient has a history of liver disease. Check transaminase levels at baseline, and continue monitoring every 6-12 months during therapy.
Educate patients on recognizing symptoms of potential side effects such as unexplained muscle pain, weakness, or dark urine. Advise them to report these symptoms immediately for further evaluation. Encourage open communication regarding any other medications or supplements that could interact with lovastatin.
Review concomitant medications regularly. Some drugs may increase the risk of adverse effects when taken with lovastatin, including certain antibiotics, antifungals, and other lipid-lowering agents.
Adjust dosages based on the individual response and tolerance. Ensure patients understand the importance of adherence to prescribed dosages and the risks of discontinuing therapy without consulting their healthcare provider.
Incorporate lifestyle modifications into the follow-up plan. Encourage dietary changes, regular physical activity, and weight management to optimize cholesterol levels alongside medication.